Photomultipliers: Difference between revisions
From ift
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
!Description | !Description | ||
!Typical Value (Fast PTM) | !Typical Value (Fast PTM) | ||
!H6780-02 | |||
|- | |- | ||
|Rise Time (TR) | |Rise Time (TR) | ||
|The time interval between the arrival of photon at the cathode and the arrival of the amplified pulse at the anode | |The time interval between the arrival of photon at the cathode and the arrival of the amplified pulse at the anode | ||
|0,05 (MCP) to 3 ns | |0,05 (MCP) to 3 ns | ||
|0,78 ns (0,2 s settling time) | |||
|- | |- | ||
|Transit Time (TT) | |Transit Time (TT) | ||
|The time interval between the arrival of photon at the cathode and the arrival of the amplified pulse at the anode | |The time interval between the arrival of photon at the cathode and the arrival of the amplified pulse at the anode | ||
|MCP:0,5 ns. PMT: 5-30 ns | |MCP:0,5 ns. PMT: 5-30 ns | ||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
|Transit Time Spread (TTS) | |Transit Time Spread (TTS) | ||
Latest revision as of 08:01, 14 April 2009
Critical Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Typical Value (Fast PTM) | H6780-02 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rise Time (TR) | The time interval between the arrival of photon at the cathode and the arrival of the amplified pulse at the anode | 0,05 (MCP) to 3 ns | 0,78 ns (0,2 s settling time) |
| Transit Time (TT) | The time interval between the arrival of photon at the cathode and the arrival of the amplified pulse at the anode | MCP:0,5 ns. PMT: 5-30 ns | |
| Transit Time Spread (TTS) | Considered as the most important specification for time-resolved measurements; the timing variation due to the different geometric paths that the electrons can take from the cathode to the anode | MCP: 0,025 ns. PMT: 0,2-1,5 ns |
Overview of different PMT's
| Part ID | Type | Driving Voltage | Gain | Spectral Range (nm) | Spectral Peak (nm) | Dark Current (after 30 min) | Rise Time (ns) | Transit Time (TT)(ns) | Transit Time Spread (TTS) (ns) | Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1161 | PMT - Head On | 1000 V | 1,0E+06 | 300 to 650 | 420 | 1-6 nA | 2,5 | 27 | 2,8 | x |
| R5505 | PMT - Head On | 1750 V | 1,0E+06 | 300 to 1400 | 900 | 10 nA | 3 | 23 | 1,5 | 16 010 SEK |
| R3478 | PMT - Head On | 1700 V | 1,7E+06 | 300 to 650 | 420 | 6 nA | 1,3 | 14 | 0,36 | 3 837 SEK |
| 7400U-02 | PMT - Head On | 800 V | 5,0E+05 | 300 to 850 | 500 | 2 nA | 0,78 | 5,4 | 0,23 | 6 404 SEK |
| R2083 | PMT - Head On | 3000 V | 2,5E+06 | 300 to 650 | 420 | 100 nA | 0,7 | 16 | 0,37 | 14 955 SEK |
| 7400-02 | PMT - Head On | 800 V | 7,0E+05 | 300 to 850 | 420 | 0,2 nA | 0,75 | 5,4 | 0,28 | 6404 SEK |
| R3809-52 | MCP - PMT | 3000 V | 2,0E+05 | 160 to 650 | 400 | 2000/s | 0,15 | 0,55 | 0,025 | 126 346 SEK |
| R5916U-52 | MCP - PMT | 3000 V | 2,0E+05 | 160 to 650 | 400 | 0,5 | 0,18 | 1 | 0,09 | 148 643 SEK |
So whats's up with the MCP's?
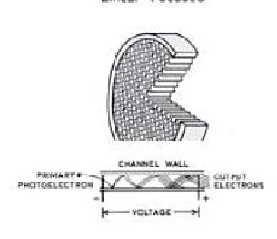
Microchannel Plate PMT, has plates containing numerous small holes, microchannels, which are lined with a secondary emissive dynode material. Electrons are amplified as they drop down the voltage gradients across the microchannel plate.
MCP-PMT shows the fastes time response due to the restricted range of electron paths and short electron travel distance.
Disadvantage is lower gain and photocurrent typ at 100 nA vs. 10-100uA for dyanode PMT